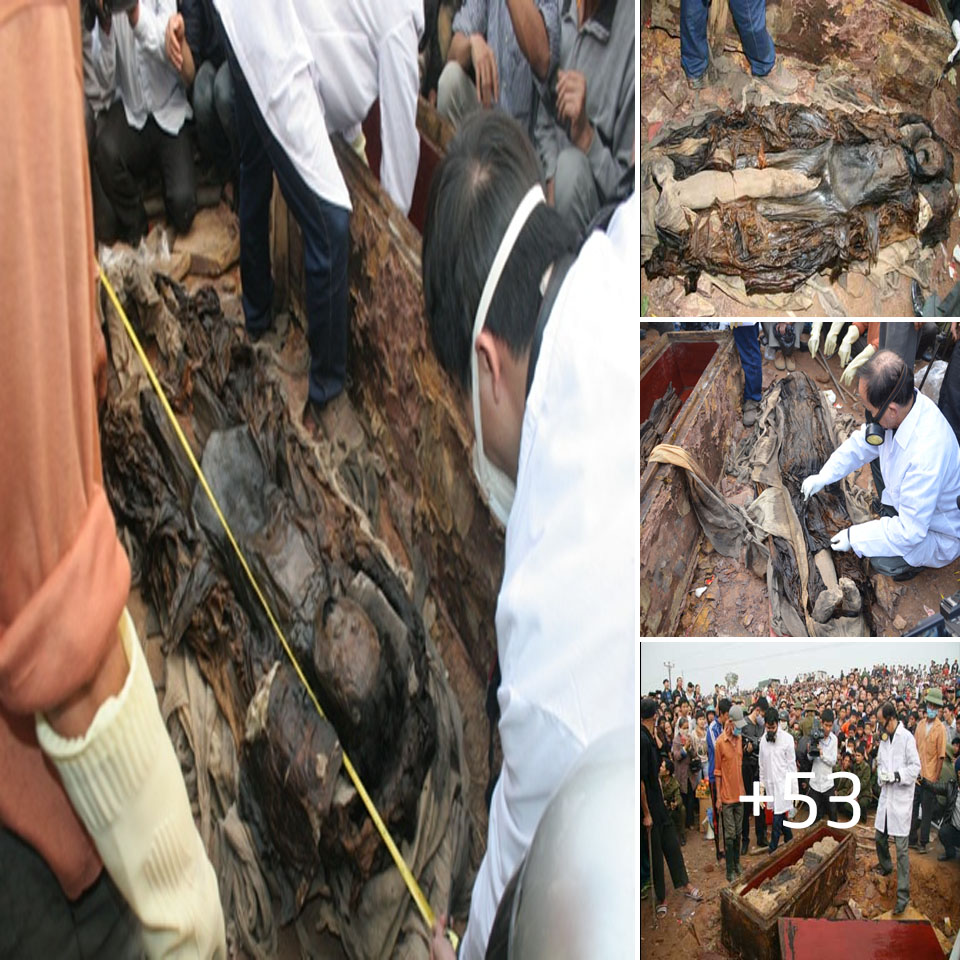
The practically entire remains of a woolly mammoth have been found in Russia by scientists. Because of their exceptional preservation, the Siberian mammoth skeletons still have flesh and hair. These remnants, which date back up to 10,000 years, could be crucial in the worldwide competition to recreate ancient animals in artificial environments.
Near the town of Seyakha, the prehistoric creature’s remains were discovered. Members of an indigenous group living near Lake Pechenelava on the Yamal Peninsula were the first to notice the discovery.

Amazing new Siberian mammoth remains
This summer has been extremely warm in Siberia, which has experienced widespread and large-scale wildfires. The Siberian mammoth remains could, however, be extracted from the permafrost thanks to the warm weather.
When the mammoth remains were discovered, specialists from the Scientific Centre for Arctic Studies arrived and started an examination. It was a fantastic discovery because they were able to recover 90% of the mammoth’s remains. According to The Daily Mail, the creature will be known as “Tadibe” in honor of its discoverer Konstantin Tadibe, a reindeer herder who resides close to the lake where the mammoth was discovered.

Russian scientists have found the almost complete remains of a mammoth in Russia
Initial investigations have revealed that the mammoth was a 10-foot-tall male teenager that died about 10,000 years ago. Evgenia Khozyainova, who took part in the study, stated that ‘We have one front and one hind foot well preserved, with tendons, soft tissues and pieces of skin,’ according to the Daily Mail.
Also found was the creature’s sacrum, some vertebrae and most of its tail, complete with pieces of skin and muscle. Archaeologist Andrey Gusev told The Siberian Times that ‘We managed to extract part of the skeleton, another part of it is still underwater and clay.’
Evidence Suggests the Mammoth Died of Natural Causes

The Siberian mammoth carcasses are so well preserved that they still have flesh and fur
The mammoth remains taken from the watery bank of the lake have been safely stored away in a special refrigeration unit. Unfortunately, the animal’s brain was not preserved which was something of a disappointment.
The Siberian Times states ‘so far there is only one preserved brain found in 2014 in Yakutia on a woolly mammoth called Yuka.’ Moreover, no tusks were retrieved in the recent find. They could have been taken by humans or simply fell off.
There is no evidence to suggest that the mammoth was killed by prehistoric hunters . Although marks on the bones indicate that at some time the remains of the prehistoric creature were scavenged. Dr Pavel Kosintsev speculates that ‘The mammoth may have become stuck in an ice crevice and been unable to escape’ reports the Daily Mail.
This Ancient Mammoth’s Soft Tissues Are Perfect for Cloning

These skeletons are up to 10,000 years old
It is exceedingly rare to find so many bones from one animal. Also found was some fossilized excrement, known as a coprolite. Dmitry Frolov, of the Arctic Research Centre, is quoted by the Daily Mail as saying that ‘The coprolite was left by this very mammoth.’ This discovery can provide scientists with considerable detail about the extinct mammoth’s eating habits.
However, this amazing find is particularly important because it provides superbly preserved dead mammoth DNA which can be used in cloning experiments . Teams, from Russia, USA, Japan, and South Korea are all desperately trying to clone ancient animals in test-tubes.

They could play an important role in the international race to recreate prehistoric beasts in the lab
The soft tissue found on Tadibe could provide the DNA key for researchers to bring woolly mammoths back to life, much like the movie Jurassic Park.The Russian federal government has funded a laboratory in Siberia to help them to win the race to clone a mammoth, which has become a matter of national prestige.
Mammoth Graveyard
Mammoths once roamed over much of Eurasia. They are closely related to modern elephants , but they were twice their size. They had remarkable tusks and trunks that could pick up even small objects.

Remains of prehistoric creatures found not far from Seyakha village
These creatures had coats of long wool that allowed them to survive in the Arctic and they were herbivores. Mammoths were hunted by men and it is believed that overhunting along with climate change contributed to the extinction of these giants of the tundra, some 4000 years ago.
The world’s most complete and best-preserved mammoth, nicknamed Lyuba, was also discovered on the Yamal Peninsula in 2007. Experts hope that the lake and the area around it will reveal many more ancient remains.
They believe that just like Tadibe, other woolly elephants died here and were forever preserved in the permafrost. There could be a mammoth graveyard hidden in the silt and water, waiting to be found.