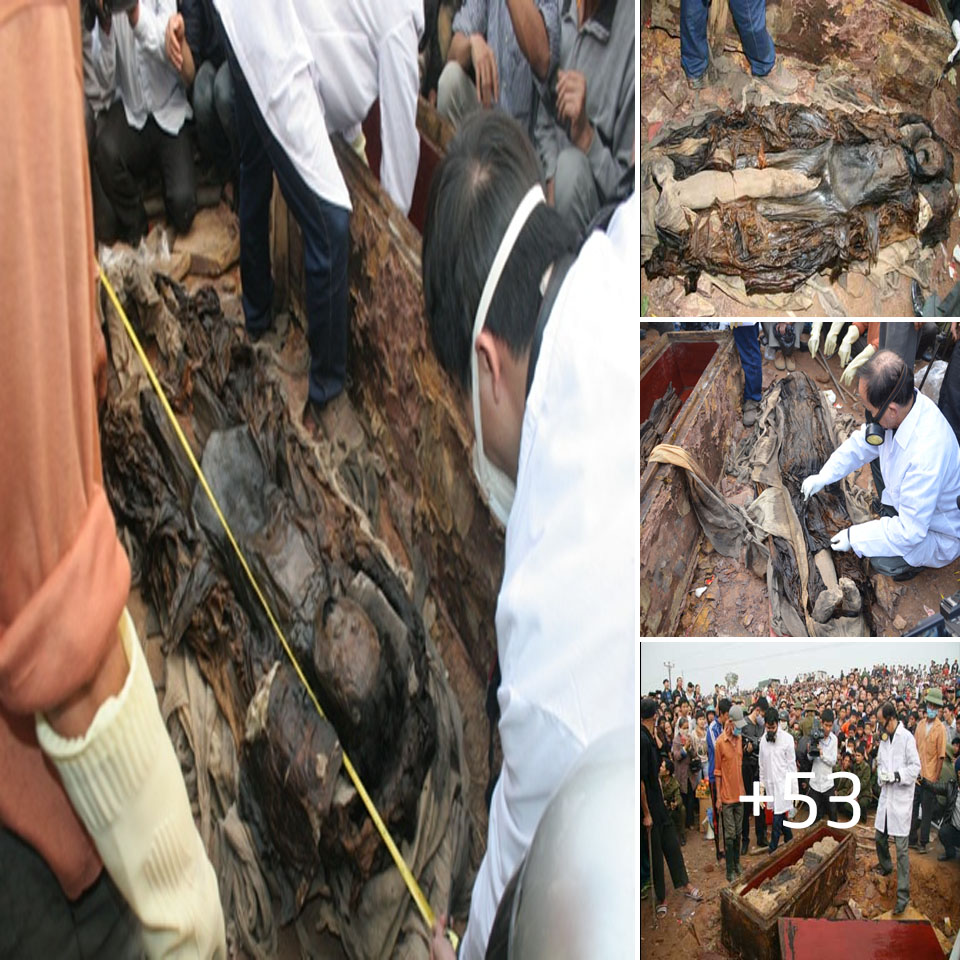
The remains of a monk, chained with iron rings has been uncovered during excavations at Khirbat el-Masani in Israel.
Khirbat el-Masani is an archaeological site, where archaeologists from the Israel Antiquities Authority previously found a tri-apsidal Byzantine-Era church, that was once part of a monastery with a road inn for travelling pilgrims.
The church is partly rock-cut and built using limestone ashlars (finely dressed stone), which may have been dedicated to Saint Zachary by the priest Sabinus.

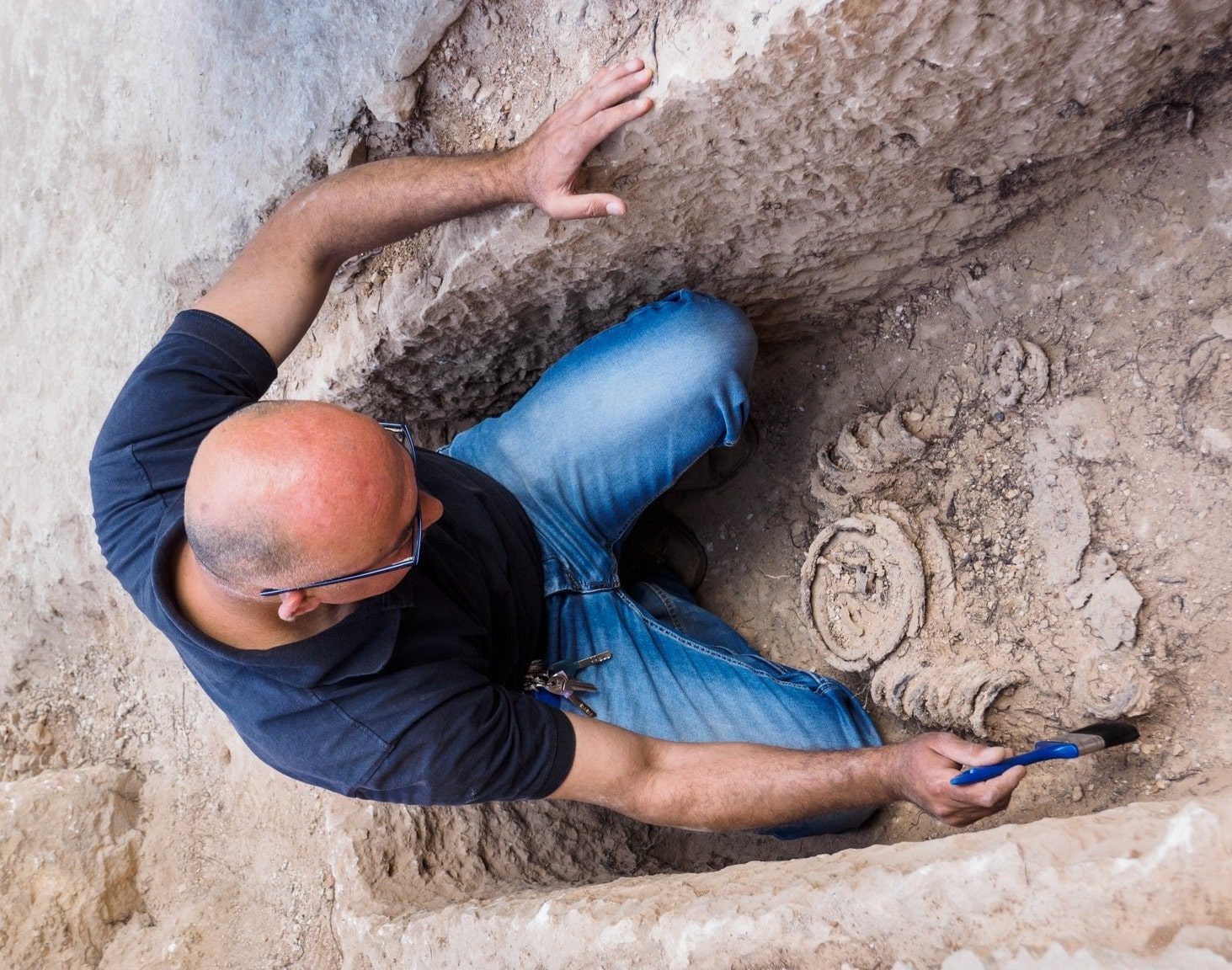
Archaeologists recently found the remains of a 1,500-year-old monk, who was buried in a cist grave next to two small niche-like closed cells in the central apse of the church. Around the neck, hands and feet of the monk are a series of iron rings weighing tens of kilograms, which the researchers suggest are symbolic of living an ascetic lifestyle, wearing the chains to prove his devotion.

Monks that followed asceticism lived a lifestyle characterised by abstinence from sensual pleasures in the pursuit of salvation, redemption from sin, or spirituality.
More extreme asceticism included the practice of chaining the body to rocks or within a cell, praying seated on a pillar in the elements, solitary confinement, abandoning personal hygiene, or self -inflicted pain and voluntary suffering.
The monk found at Khirbat el-Masani likely lived in or near the church compound, placing himself in seclusion while chained inside a secluded closed cell. The practice originates in Syria in the 4th or 5th century AD, however, the discovery of the burial shows that this form of extreme asceticism spread as far south as the Jerusalem region during the Byzantine period.

Another example was previously discovered by archaeologists during excavations at Giv’at HaMatos near the Mar Elias Monastery, located between Jerusalem and Bethlehem. Archaeologists at the time found the burial of a man wearing iron chains around the upper body in a subterranean cave consisting of two cubicles.
Src: heritagedaily.com