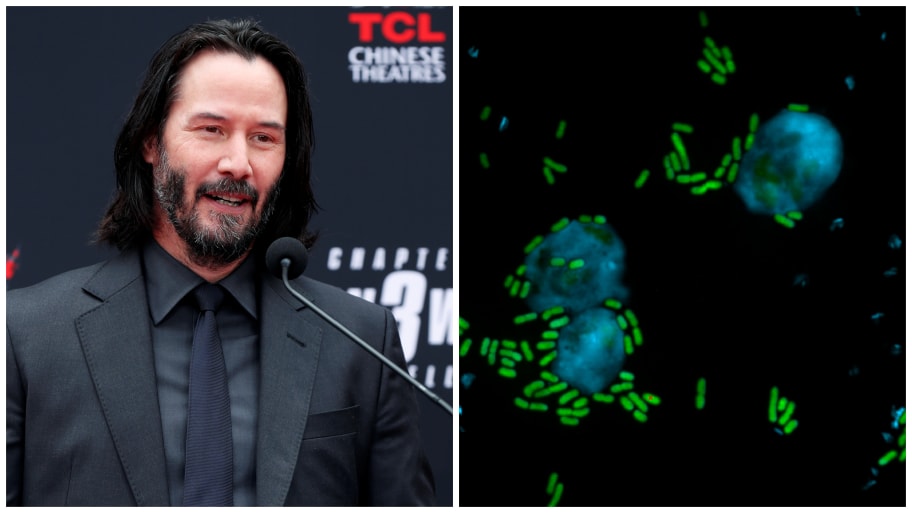
According to the scientists who discovered it, the compound is called keanumycins because it kills fungi as easily as the action heroes made by Reeves destroy enemies in movies like ‘The Matrix’ and the ‘John’ series. Wick’.
Following the release of HBO Max’s 2023 TV series adaptation of the hit video game “The Last of Us,” about a zombie apocalypse caused by a mushroom pandemic, some wonder if mushrooms lethal could be the next environmental problem to worry about.
As CNN points out, future human fungal outbreaks are unlikely to be like what happened in “The Last of Us.” However, as the Earth’s climate warms and more and more strains of fungi develop resistance to antifungal drugs, fungal diseases in humans are bound to get worse.
Besides the effects on human health, fungal outbreaks also threaten the world’s food supply, according to an article published in the journal Nature Food .
To address this danger, science has discovered an antifungal byproduct from some bacteria that is able to fight both human and plant fungal diseases, as Phys.org reports.
When naming this new discovery, scientists had in mind one of Hollywood’s most famous and recognizable action stars: Keanu Reeves, as The Byte writes.
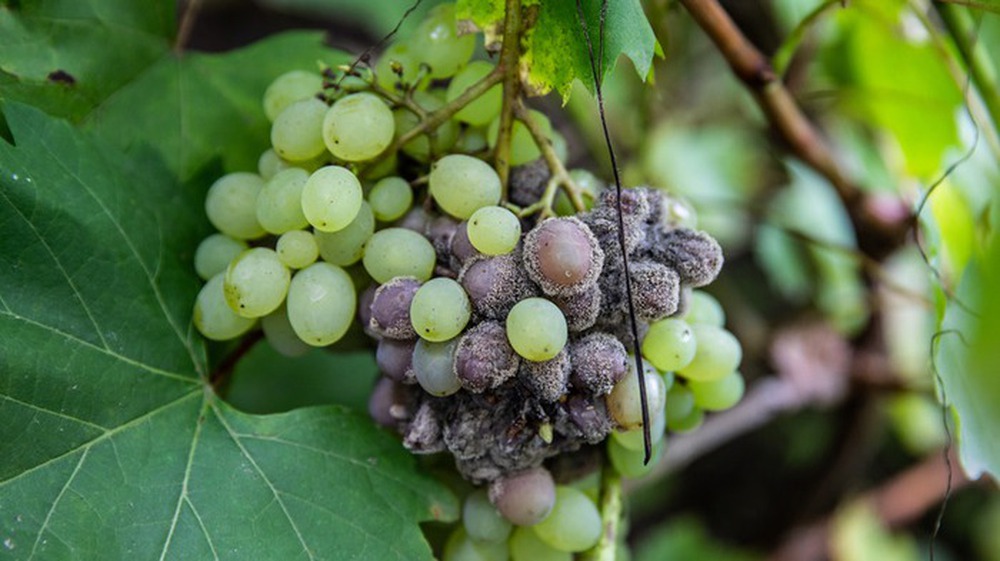

Keanumycins, made from bacteria of the genus Pseudomonas, target a plant-damaging fungus called Botrytis cinerea, which causes crop-destroying gray mold rot.
This antifungal compound was discovered by researchers at the Leibniz Institute for Infection Biology and Natural Products in Germany.
Their findings were published in a study through the Journal of the American Chemical Society (ACS). This compound, naturally produced by bacteria of the genus Pseudomonas, is effective against fungal infections in both plants and humans. Since it is produced in a completely natural way, this compound can therefore be considered an eco-friendly alternative.
Scientists have shown that the compound is particularly “effective” against the fungus Botrytis cinerea, which causes gray mold disease and causes huge annual losses.
Previous research has shown that this mold rot can cause major harvest losses in fruit and vegetable crops every year, affecting more than 200 different fruits and vegetables, especially strawberries and berries. unripe grapes.
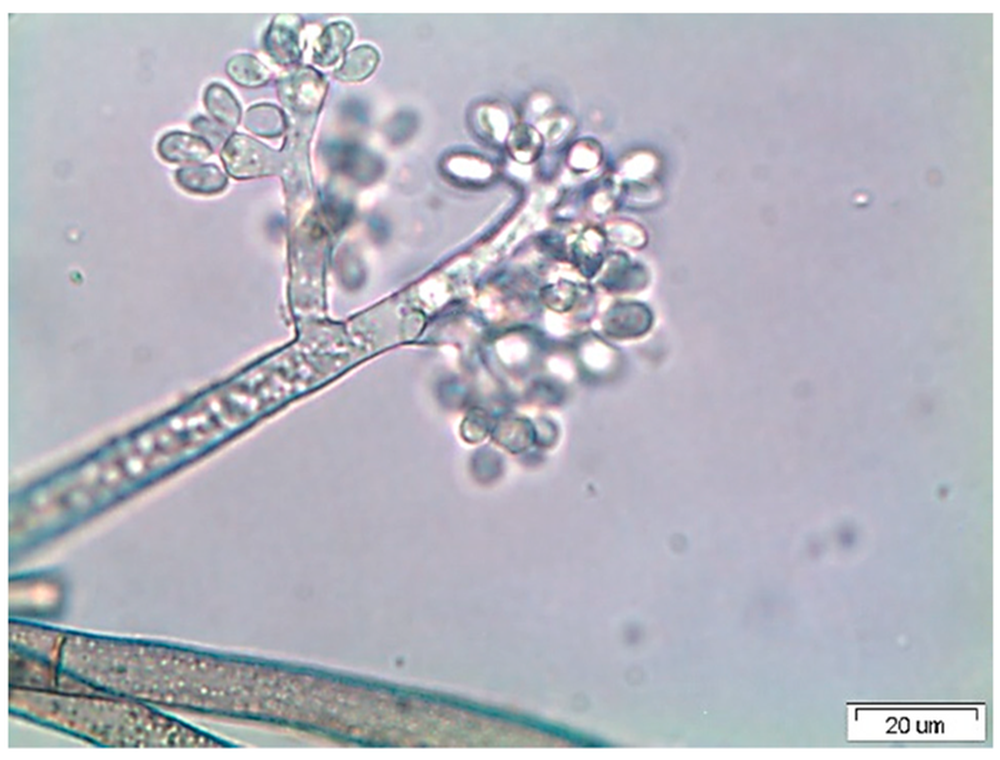
Botrytis cinerea can fly through the air and perch on different plants. It has been known to infect more than 200 species of plants.
Studies have also found that this compound can also inhibit the growth of fungi that are dangerous to humans such as Candida albicans, a yeast that causes thrush in humans.
The new compound could be an “environmentally friendly alternative” to chemical pesticides, the study says, and could also offer an alternative in the fight against resistant fungi.
Regarding the significance of this finding, study author Sebastian Götze said: “We are facing an antifungal crisis… Many fungi that cause disease in humans are now resistant to antifungal drugs – in part because They are used in large quantities in the agricultural sector.

When researchers tested the natural product isolates against fungi infecting humans, they found that it “strongly inhibits” the fungus that causes the disease Candida albicans.
This new antifungal compound is so effective that when it comes to naming it, they chose “keanumycin” in honor of Keanu Reeves, the action star of the “John Wick” and “Matrix” action series.
Regarding their decision to call their finding keanumycin, Leibniz Institute researcher Sebastian Götze said the group of lipopeptides have dangerous properties for fungi, “so effective that we named them after Keanu Reeves because he is also extremely active.” dangerous in his roles”.
As mentioned, these all-natural products are biodegradable and safe to use directly on plants. In addition, Götze added, “we tested this isolate against various fungi infecting humans”, with encouraging signs that keanumycin may also help fight fungal infections in humans and humans. timely.

According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 75,000 people were hospitalized with fungal infections in 2014 and about 7,000 died in 2021 — although the real number is likely much higher.